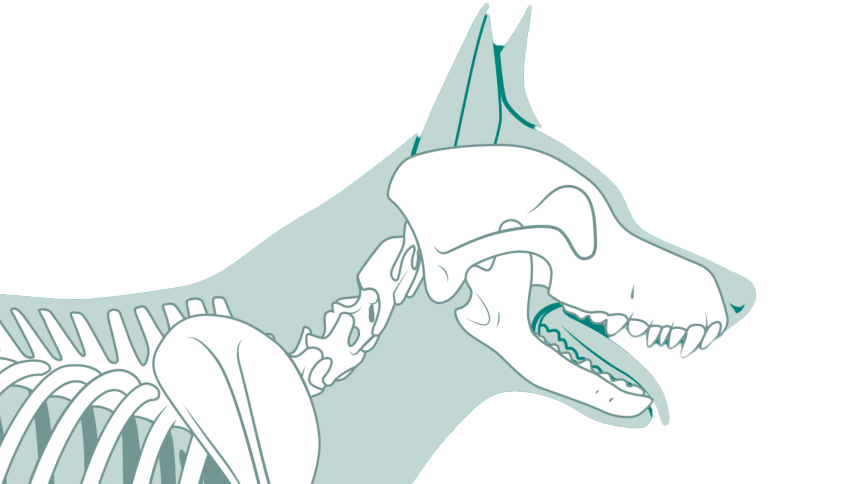
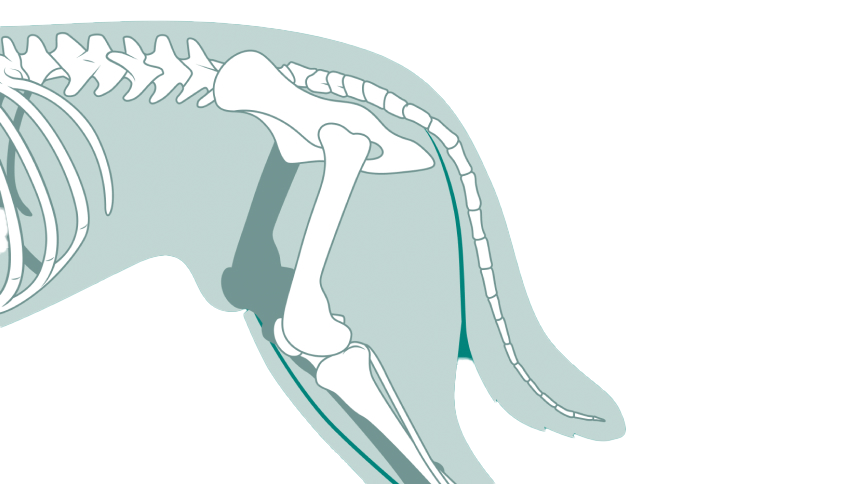
Hip dislocation, or luxation, occurs when the femoral head (the ball of the hip joint) is displaced from the acetabulum (the socket). This condition causes significant pain and lameness in pets and requires prompt intervention to restore joint function. There are two primary treatment options: closed reduction and open reduction with internal fixation.
Closed reduction is a non-surgical technique where the veterinarian manually repositions the dislocated hip. This procedure is performed under anesthesia to ensure the pet’s comfort. The femoral head is guided back into the acetabulum using specific maneuvers. After successful repositioning, the hip is often stabilized with a sling or bandage to prevent re-dislocation while the surrounding tissues heal. Closed reduction is typically suitable for recent dislocations where there is minimal damage to the surrounding structures.
Open reduction with internal fixation is a surgical approach used for severe or recurrent hip dislocations. This procedure involves surgically exposing the hip joint, repositioning the femoral head into the acetabulum, and securing it with pins, screws, or plates to ensure stability. This method is often chosen when there is significant damage to the joint capsule or surrounding tissues, or when closed reduction has failed.
Closed Reduction
- Suitable for recent dislocations.
- Ideal for pets with minimal damage to the joint capsule and surrounding tissues.
- Preferred for pets where a non-surgical approach is deemed sufficient.
Open Reduction with Internal Fixation
- Necessary for severe or recurrent dislocations.
- Suitable for pets with significant damage to the joint capsule or surrounding tissues.
- Recommended when closed reduction is unsuccessful or not feasible.
The diagnosis of hip dislocation typically involves a thorough physical examination and imaging techniques such as X-rays to confirm the dislocation and assess the extent of any associated damage. Once the appropriate treatment method is determined, a comprehensive pre-surgical evaluation is performed to ensure the pet is a suitable candidate for anesthesia and surgery.
- Strict rest and limited activity to allow the hip to heal.
- Use of a sling or bandage to stabilize the hip.
- Follow-up visits to monitor healing and ensure the hip remains in place.
- Strict rest and controlled activity to promote healing.
- Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint.
- Regular follow-up visits to monitor the recovery process and check the stability of the hip.
With appropriate treatment and post-operative care, pets can achieve significant improvements in hip function and overall mobility, enhancing their quality of life.
Our areas of expertise
Transforming the way orthopedic care is delivered
For Vets
Refer your patients to our specialists using our streamlined online portal.
Referral portalFor Pets
Request a consultation or prepare for surgery with us and experience expert compassionate care every step of the way.
Request a consultation