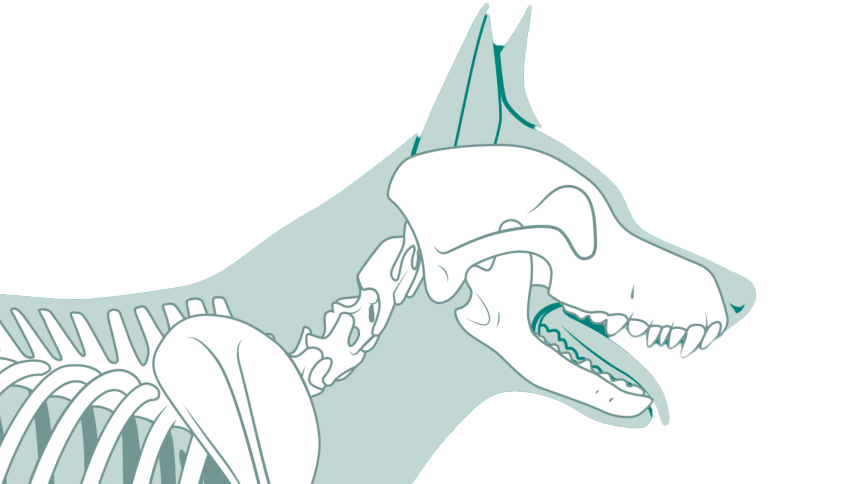
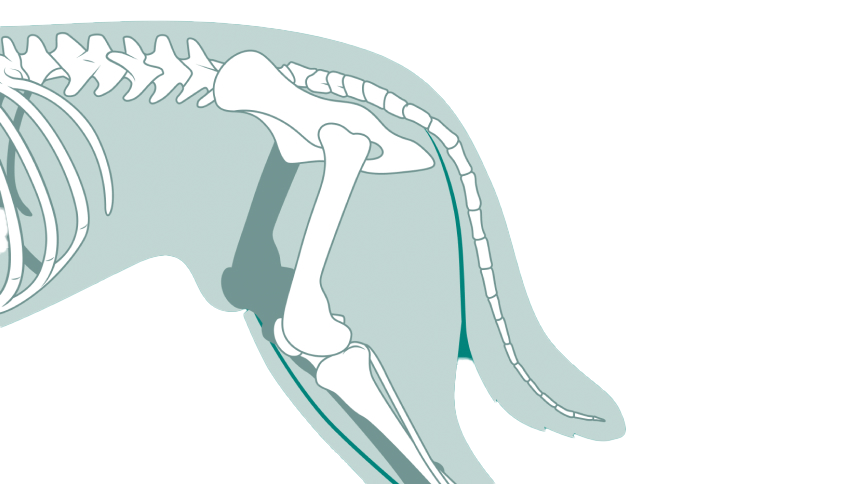
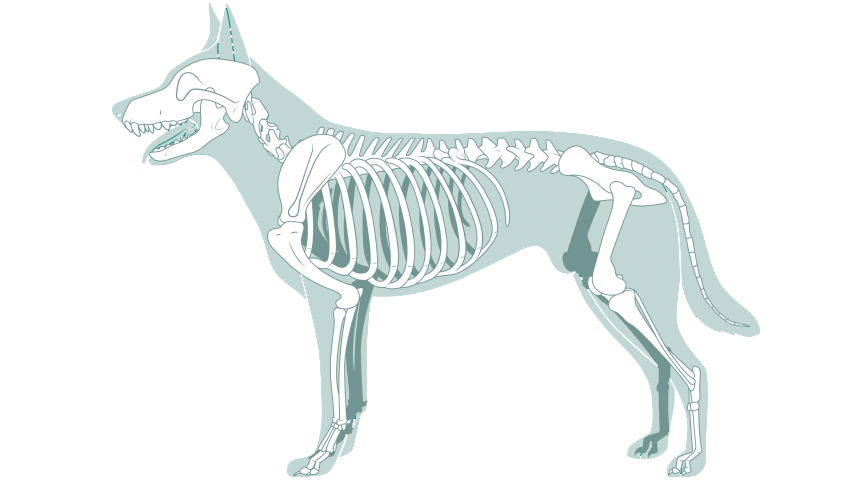
Fractures in small animals, such as cats and dogs, are often caused by accidents, falls, or other trauma. They range from simple, clean breaks to complex fractures involving multiple bone segments. Without proper treatment, fractures can lead to severe pain, loss of limb function, and long-term complications like arthritis or malunion. Fracture repair involves surgical intervention to stabilize the bone, ensuring it heals correctly and fully. Veterinary surgeons assess each case individually to determine the best repair method based on the location, severity, and type of fracture.
Fracture repair techniques are tailored to the individual pet’s needs, with a focus on precision and stability.
- Internal Fixation:
Internal fixation involves using plates, screws, pins, or rods to stabilize the bone from within. This technique is ideal for simple or straightforward fractures where internal hardware can securely hold the bone fragments together. - External Fixation:
For complex or open fractures, external fixators may be used. These devices consist of pins inserted into the bone and connected to external rods, providing stability and allowing for adjustments during the healing process. External fixation is especially useful for fractures with significant soft tissue damage. - Minimally Invasive Approaches:
Advanced imaging and minimally invasive surgical techniques reduce tissue disruption during fracture repair. This results in faster recovery times and improved outcomes for the pet.
Fracture repair is suitable for pets of all ages and sizes experiencing broken bones due to trauma or other causes. Early intervention is critical to ensure proper healing and prevent complications like malunion or infection. Factors such as the pet’s overall health, age, and fracture location are considered when determining the most appropriate repair method. In older pets, pre-existing conditions like arthritis may influence the surgical approach.
Diagnosis of fractures typically involves physical examinations, X-rays, and occasionally CT scans to assess the extent and complexity of the break. Once surgery is planned, a thorough preoperative evaluation ensures the pet is fit for anesthesia. Post-surgery, pets require careful monitoring and follow-up appointments to assess healing progress. Rehabilitation, including controlled activity, physical therapy, and pain management, plays a crucial role in recovery. With proper care, most pets regain full function of the affected limb, enjoying improved mobility and quality of life.
Our areas of expertise
Transforming the way orthopedic care is delivered
For Vets
Refer your patients to our specialists using our streamlined online portal.
Referral portalFor Pets
Request a consultation or prepare for surgery with us and experience expert compassionate care every step of the way.
Request a consultation